NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide reduced form)
Description
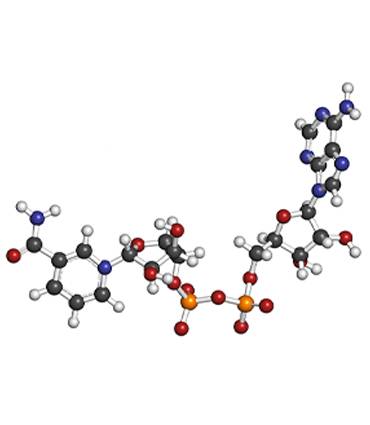
A molecule present in the body's cells, NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is involved in the proper functioning of biological processes. NADH is considered a coenzyme, a molecule that is essential for the activity of certain enzymes.
NADH is made up of an assembly of two nucleotides, one of which corresponds to adenine and the other to nicotinamide. NADH is synthesised from vitamin B3, but also from two amino acids: aspartate and tryptophan.
The importance of this coenzyme comes from the fact that it can be found in its oxidised form NAD+, or in its reduced form NADH. Thus, NADH is involved in chemical redox reactions, particularly in cellular respiration. In biology, cellular respiration is an essential process by which the oxidation of glucose leads to the production of the energy necessary for the functioning of cells.
The benefits
NADH is a coenzyme involved in cellular respiration and the creation of energy, which are essential for the functioning of cells.
Scientific publications
NADH is the subject of more than 29 528 scientific publications.
Our products based on NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide reduced form)
-
€38.90











